Risk Factors
Risk factors for Hypercholesterolemia (And cardiovascular disease): the diabetes, The hypertension, The obesity, The smoking and lack of exercise; Diets rich in Saturated fat (Animal) and trans (Partially hydrogenated vegetable fats, found in many processed products) and cholesterol, A family history of Hypercholesterolemia at an early age, family history of heart disease ...
No symptoms
The problem of Hypercholesterolemia is noteworthy that no symptoms. A blood test is the only way to detect it. Experts recommend a Cholesterol test at 20 years of age and then every 5 years. More frequent tests are recommended if the patient has a family history of Hypercholesterolemia or other risk factors, as smoking or diabetes.
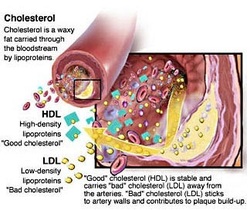
"Good" cholesterol and "bad" cholesterol
In order to circulate in the blood (an aqueous medium), the cholesterol (A type of fat) is bound to proteins. This combination is known as lipoprotein. Three types of lipoprotein:
1. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL, for its acronym in English). The LDL or "bad" cholesterol transports cholesterol particles throughout the body. Excess LDL cholesterol builds up in artery walls and ends up hardening and narrowing the arteries (atherosclerosis).
2. Very low density lipoprotein - This type of lipoprotein takes the maximum associated triglycerides (Another type of fat in the blood, also associated with cardiovascular risk). Like the LDL, The VLDL causes narrowing of the arteries.
3. High density lipoprotein (HDL). The HDL or "good" cholesterol acts as a plunger, removing excess LDL cholesterol HDL cholesterol rates, the lower the cardiovascular risk. Lipid profile. Values total cholesterol above 200 mg / dl and values of LDL ("bad") of over 160 mg / dl an increasing risk of heart attacks and strokes. In turn, HDL ("good cholesterol) above 45 mg / dl significantly reduces that risk. Known as lipid tests, The Cholesterol test values usually include total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
Impact
The Hypercholesterolemia is the eve of the atherosclerosis, Dangerous buildup of plaque within the arteries. If the affected atherosclerosis are those that supply blood to the heart (coronary arteries) can cause chest pain (angina).
If arterial plaque breaks or cracks can form a blood clot (thrombus) in the place of rupture and block blood flow there or travel freely and block an artery elsewhere.
A heart attack is a consequence of the interruption of blood flow from the heart. Stroke occurs when blood supply ceases to part of the brain.
Treatment
Changes in diet, regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking ... help maintain cholesterol at bay. As for food, we recommend a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables and low in saturated and trans fats and refined flours and sugars. As fats are advisable virgin olive oil, nuts and oily fish.
Get free consultation online - 24 Hour's Free Support at Herbalcureindia.com/free-consultation.htm to prevent cardiovascular disease, natural treatment for heart problem and high blood pressure.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed